Repowering Stony Brook
Project Information
Year: Fall 2020
Course: Energy Systems Design
Group Members: Jamaal Lake, Bajinder Singh, Misbah Syeda, Jhun Martinez
Time: 3 months
Task
Each team will design a plant based on the thermodynamic cycles and technologies learned in class. You have the freedom to be creative and need not concern yourselves with economics. However, the design must be realistic!
Deliverables
I handled the scripting and design of our presentation.
The Project
To repower the current simple cycle co-generation Stony Brook Power Plant into a combined cycle.
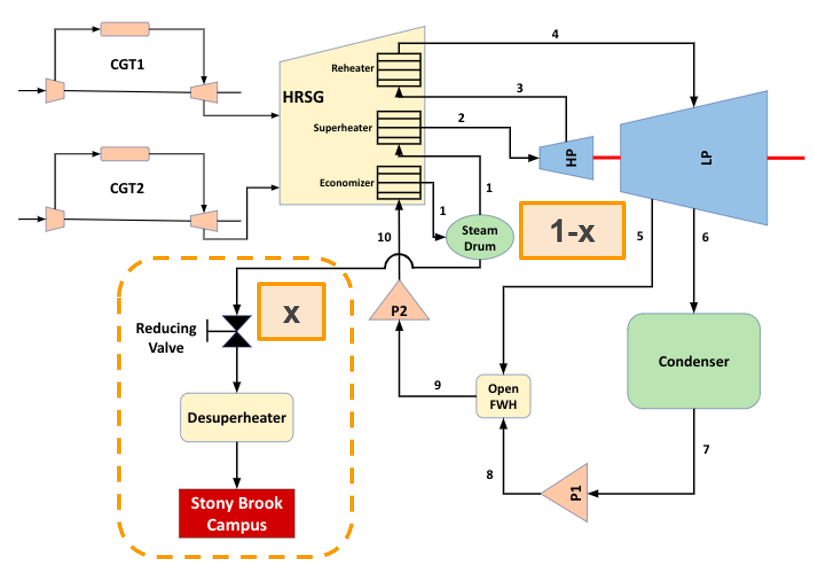
Schematic
The schematic of the repowered combined cycle power plant.
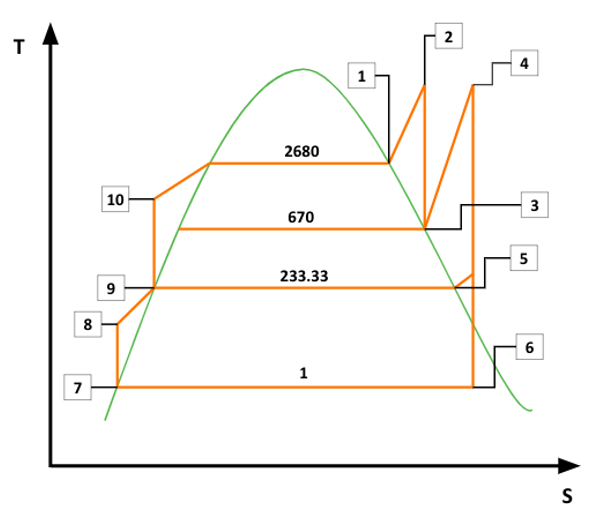
T-S Diagram
The T-S diagram for the plant in the schematic above was drawn.
The steam turbine inlet pressure was 2680 psi.
The reheat pressure was 670 psi.
The feedwater heater inlet pressure was 233 psi.
The condenser inlet pressure was 1 psi.
Calculations
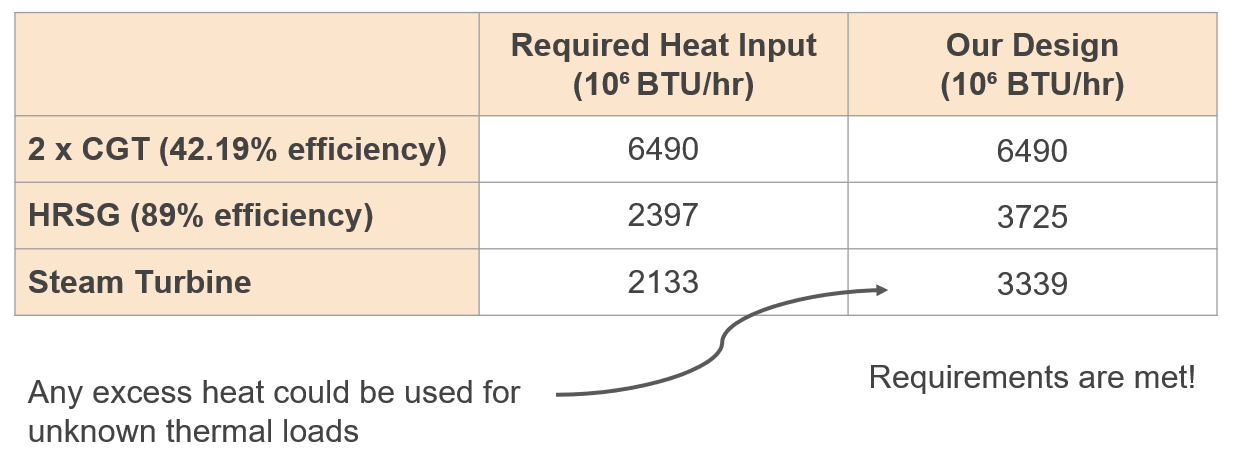
The Stony Brook Power Plant is a co-generation power plant, meaning that it generates both heat and steam. The summer season however does not require heating, and therefore the process of sending heat to the campus was only calculated for the winter.
Winter Heat Calculations
During the winter, some of the steam generated by the heat recovery steam generator is sent to the campus to obtain the following heat distributions:
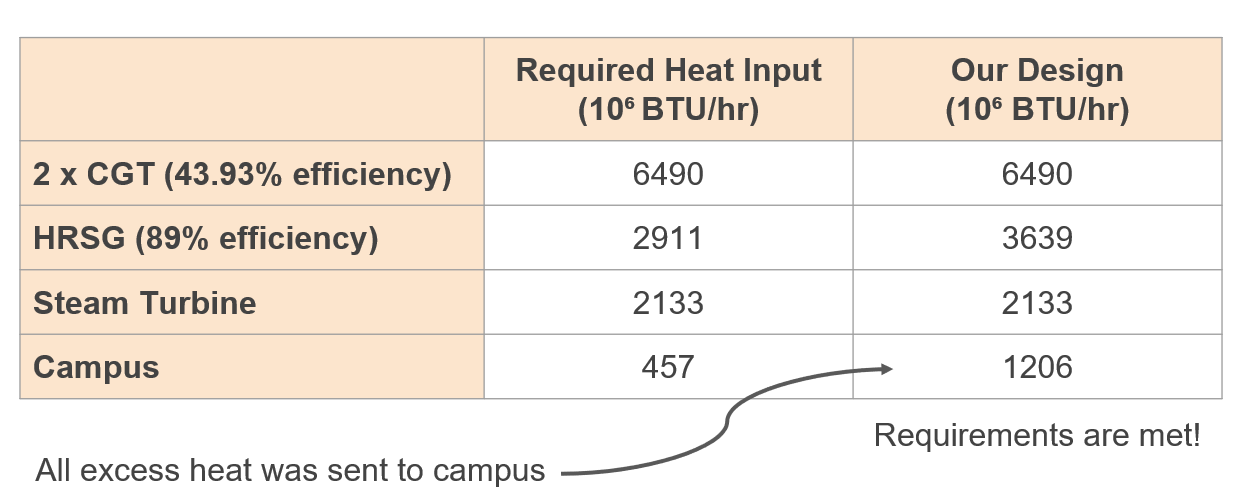
Summer Heat Calculations
Since during the summer season, the campus does not require heat, all of the steam generated by the heat recovery steam generator could be sent to the steam turbine. However, since there is an excess, some of that heat could be used for additional loads outside the scope of our projects if necessary.
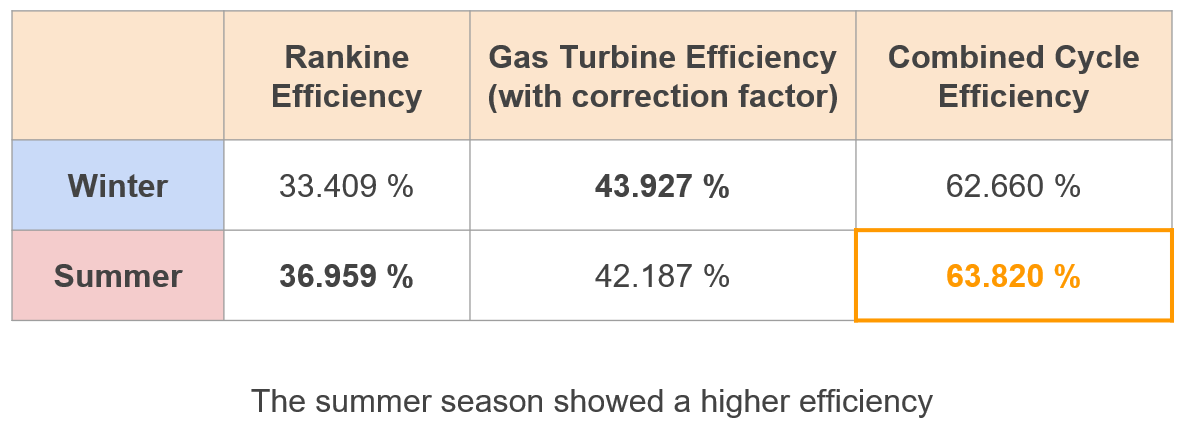
Cycle Efficiency
The cycle efficiency was determined:
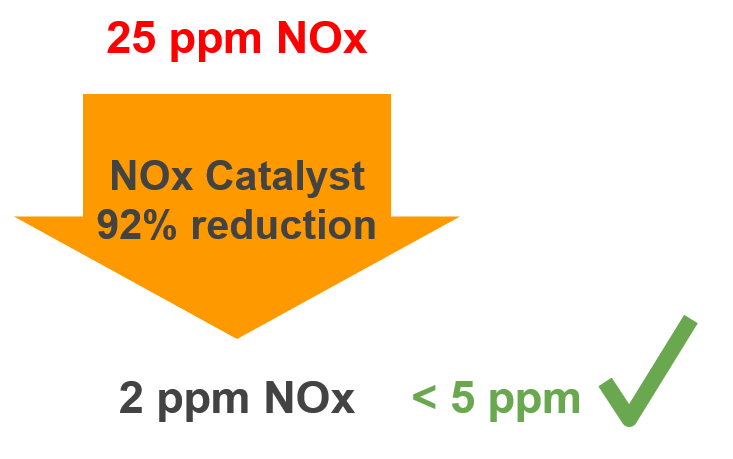
Environmental Impact Statement
The level of CO in our design was 10 ppm as obtained from the technical specifications. The level of NOx in our design was 25 ppm similarly. Since these were both very high values, they had to be reduced to acceptable levels of 0.1 ppm CO and 5 ppm NOx. We did that using CO and SCR catalysts placed inside our HRSG.

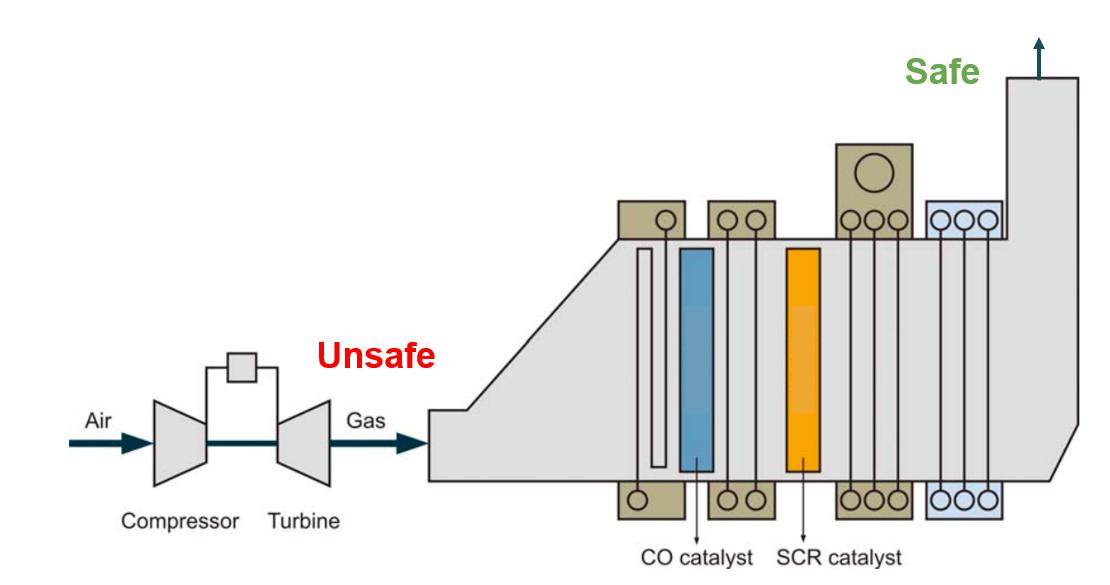
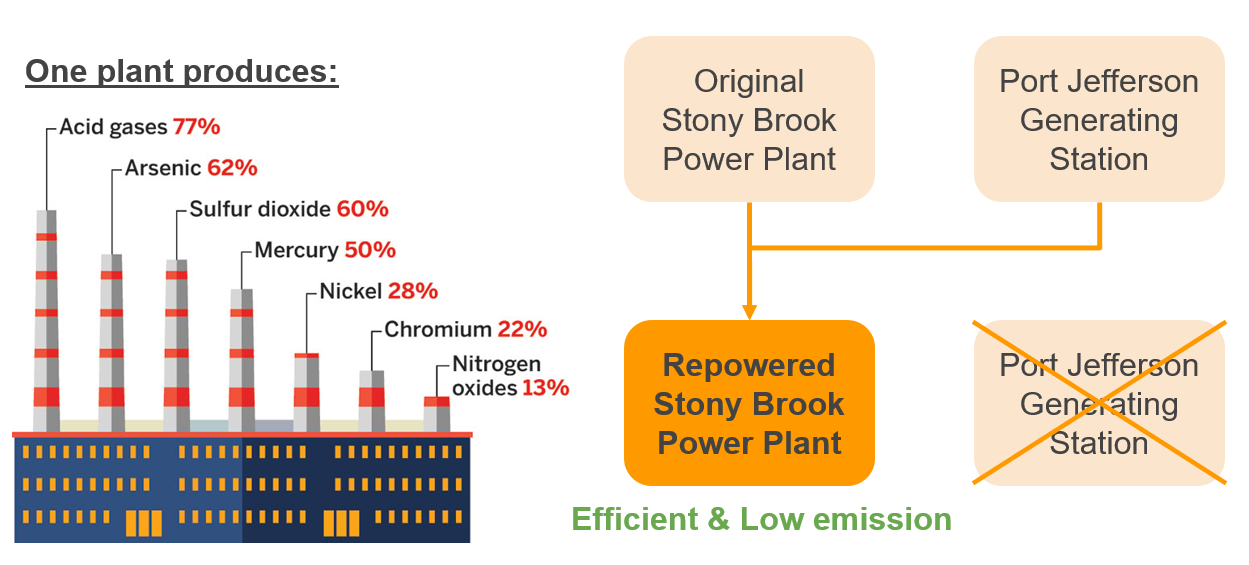
We have concluded that we could get rid of the Port Jefferson Generating Station nearby because we generate excess energy at a higher efficiency. This allows us to have a single fuel-efficient and low emission power plant rather than two less efficient high emission plants.
Conclusion
We have concluded that we will have a surplus of 926 MW and an efficiency 16% higher than that of Port Jefferson Generating Station.